qacReg for Logistic Regression
logistic.RmdIn this analysis, we’ll develop a model for predicting births by
caesarian from patient characteristics uing the caesarian
data frame.
Model fitting is normally an iterative process. We’ll skip this to keep things simple.
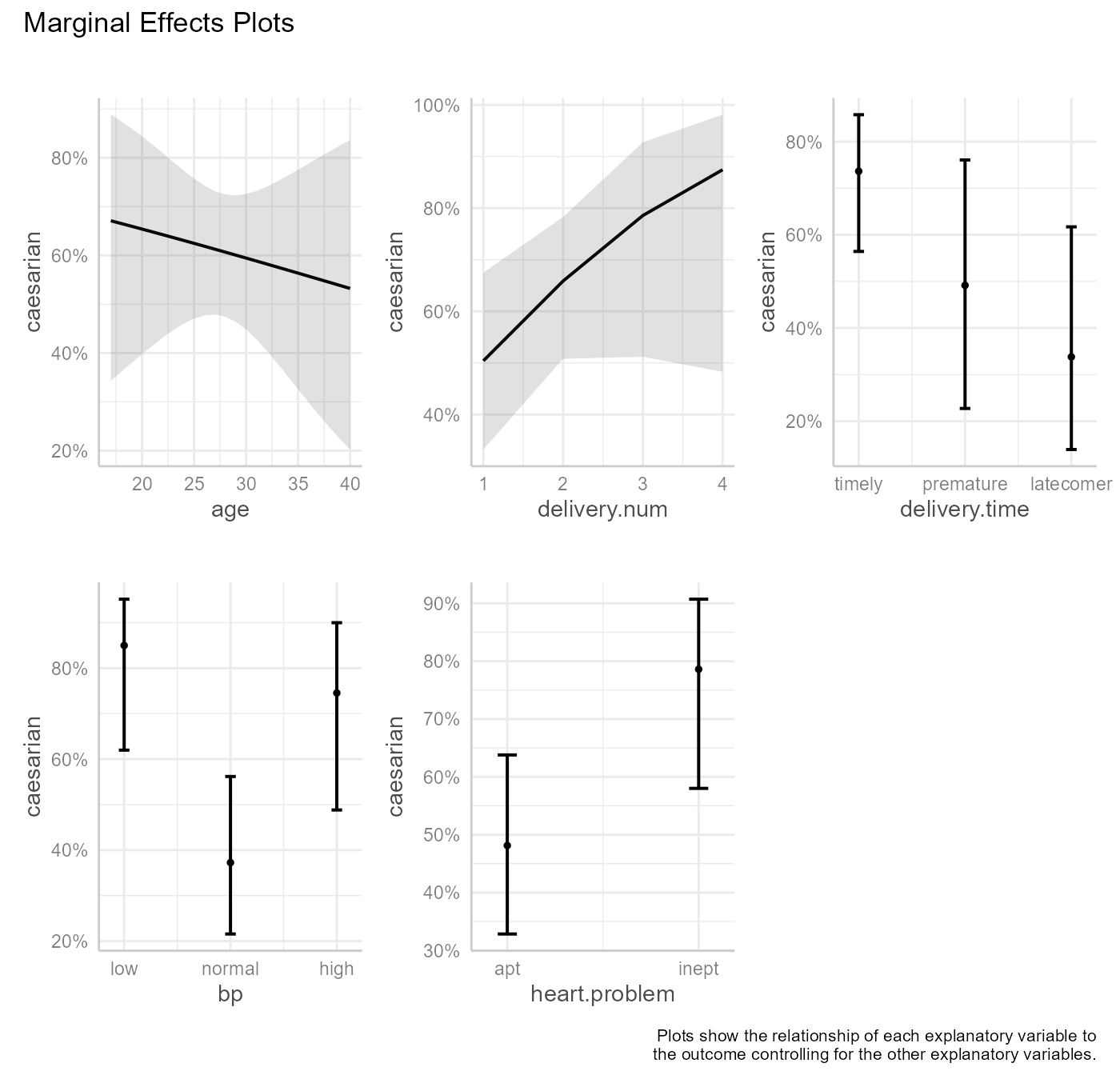
Examine the model
info(fit)
#> LOGISTIC REGRESSION SUMMARY
#> Formula: caesarian ~ .
#> Data : caesarian
#> N : 80
#>
#> Predicted category: yes
#>
#> Omnibus Test
#> Chi-square(7) = 24.5557, p = 0.0009094 ***
#>
#> Fit Measures
#> Stukel's GOF Test: Chi-square(2) = 2.7587, p < 0.2517
#> Tjur's Psuedo-R.squared: 0.2715
#> AIC: 100.541
#>
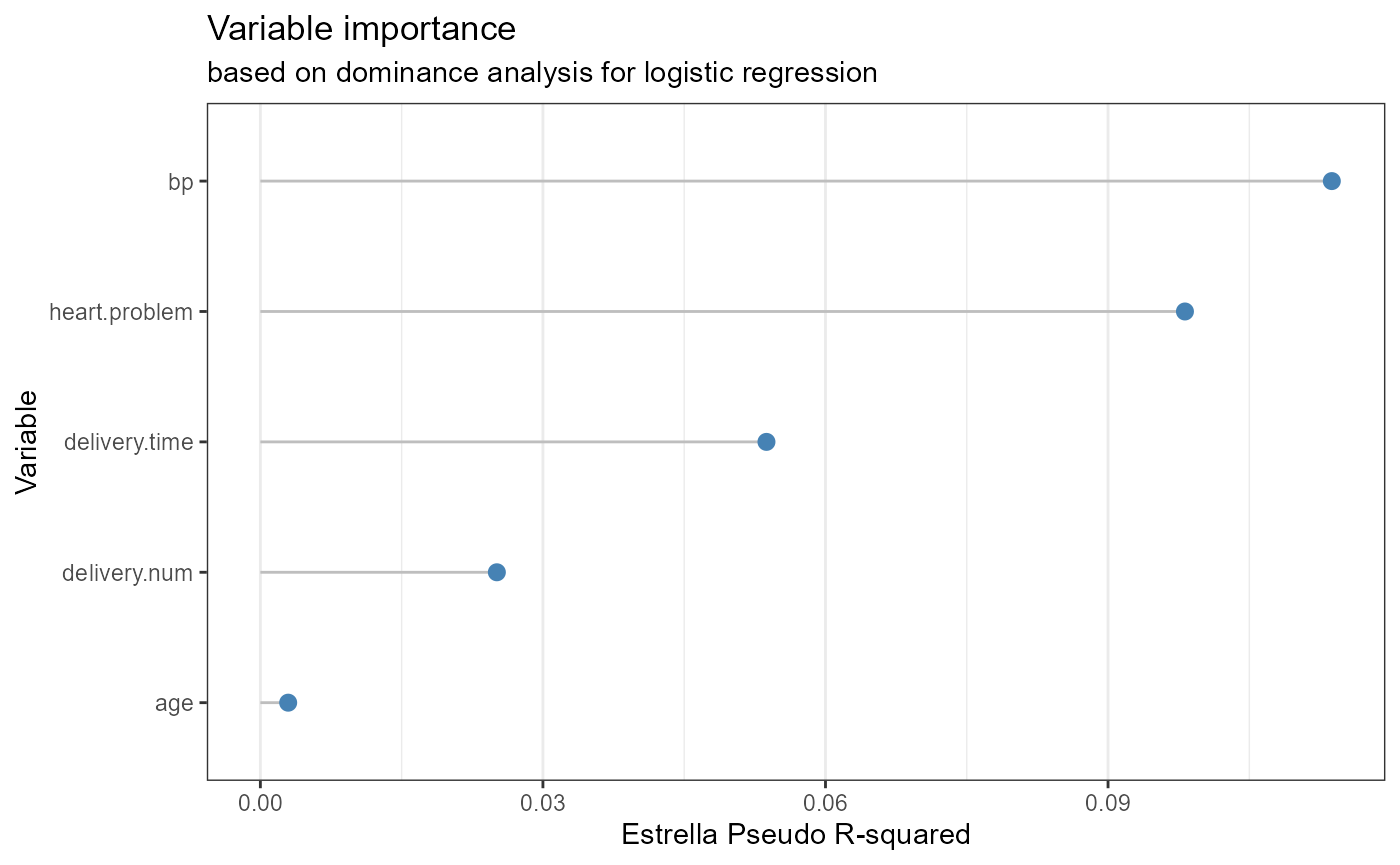
#> Anova Table (type III tests)
#> LR Chisq DF Pr(>Chisq)
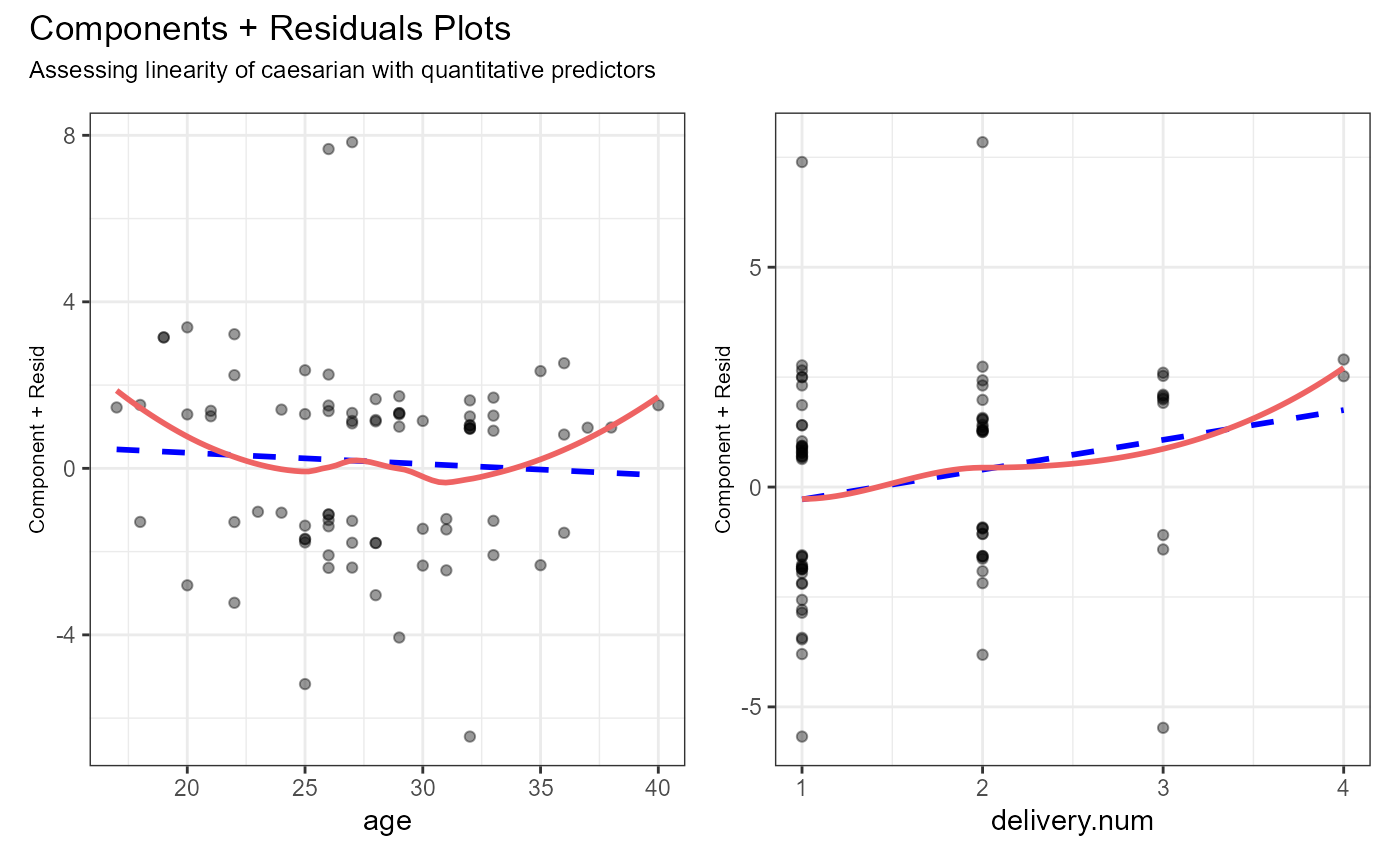
#> age 0.1874 1 0.665107
#> delivery.num 2.6039 1 0.106598
#> delivery.time 6.3377 2 0.042052 *
#> bp 10.9374 2 0.004217 **
#> heart.problem 5.6196 1 0.017761 *
#>
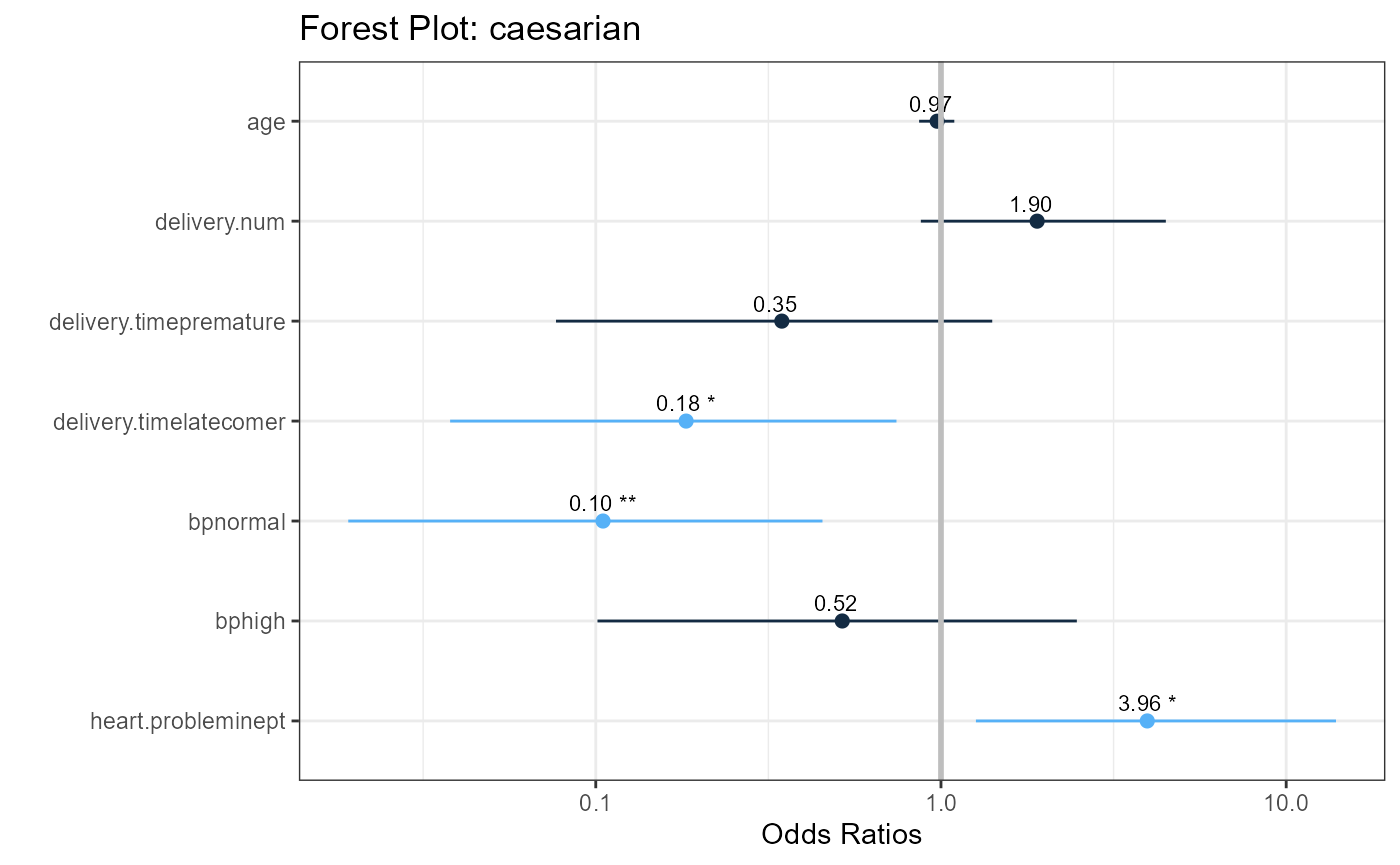
#> Logistic Regression Coefficients
#> B SE z Pr(>|z|)
#> (Intercept) 1.43912 1.60133 0.8987 0.368811
#> age -0.02534 0.05883 -0.4307 0.666678
#> delivery.num 0.64139 0.41054 1.5623 0.118218
#> delivery.timepremature -1.06162 0.73059 -1.4531 0.146193
#> delivery.timelatecomer -1.70004 0.74871 -2.2706 0.023170 *
#> bpnormal -2.25423 0.79667 -2.8296 0.004661 **
#> bphigh -0.65859 0.80363 -0.8195 0.412491
#> heart.probleminept 1.37590 0.60431 2.2768 0.022797 *
#>
#> Odds Ratios (with 95% Confidence Intervals)
#> Odds Ratio 2.5% 97.5%
#> age 0.9750 0.86430 1.0930
#> delivery.num 1.8991 0.87428 4.4808
#> delivery.timepremature 0.3459 0.07670 1.4076
#> delivery.timelatecomer 0.1827 0.03786 0.7431
#> bpnormal 0.1050 0.01919 0.4536
#> bphigh 0.5176 0.10116 2.4749
#> heart.probleminept 3.9586 1.26252 13.9405Assess predictive performance
performance(fit)
#> LOGISTIC REGRESSION PERFORMANCE
#> Data : caesarian
#> N : 80
#> Response variable : caesarian
#> Category Balance : no (0.42%) yes (0.58%)
#> Predicted category: yes
#> Prob to classify : >=0.5
#>
#> Model: glm(caesarian ~ .,
#> family = binomial, data = caesarian)
#>
#> Confusion Matrix
#>
#> Actual
#> Predicted no yes
#> no 22 11
#> yes 12 35
#>
#> Overall Statistics
#>
#> Accuracy: 0.7125
#> 97% CI : (0.6005, 0.8082)
#> No Information Rate: 0.575
#> P-Value [Acc > NIR]: 0.007869
#>
#> Statistics by Category
#>
#> Sensitivity 0.7609
#> Specificity 0.6471
#> Pos Pred Value 0.7447
#> Neg Pred Value 0.6667
#> F1 0.7527
#> ---
#> Note: recall = sensitivity,
#> precision = pos pred value.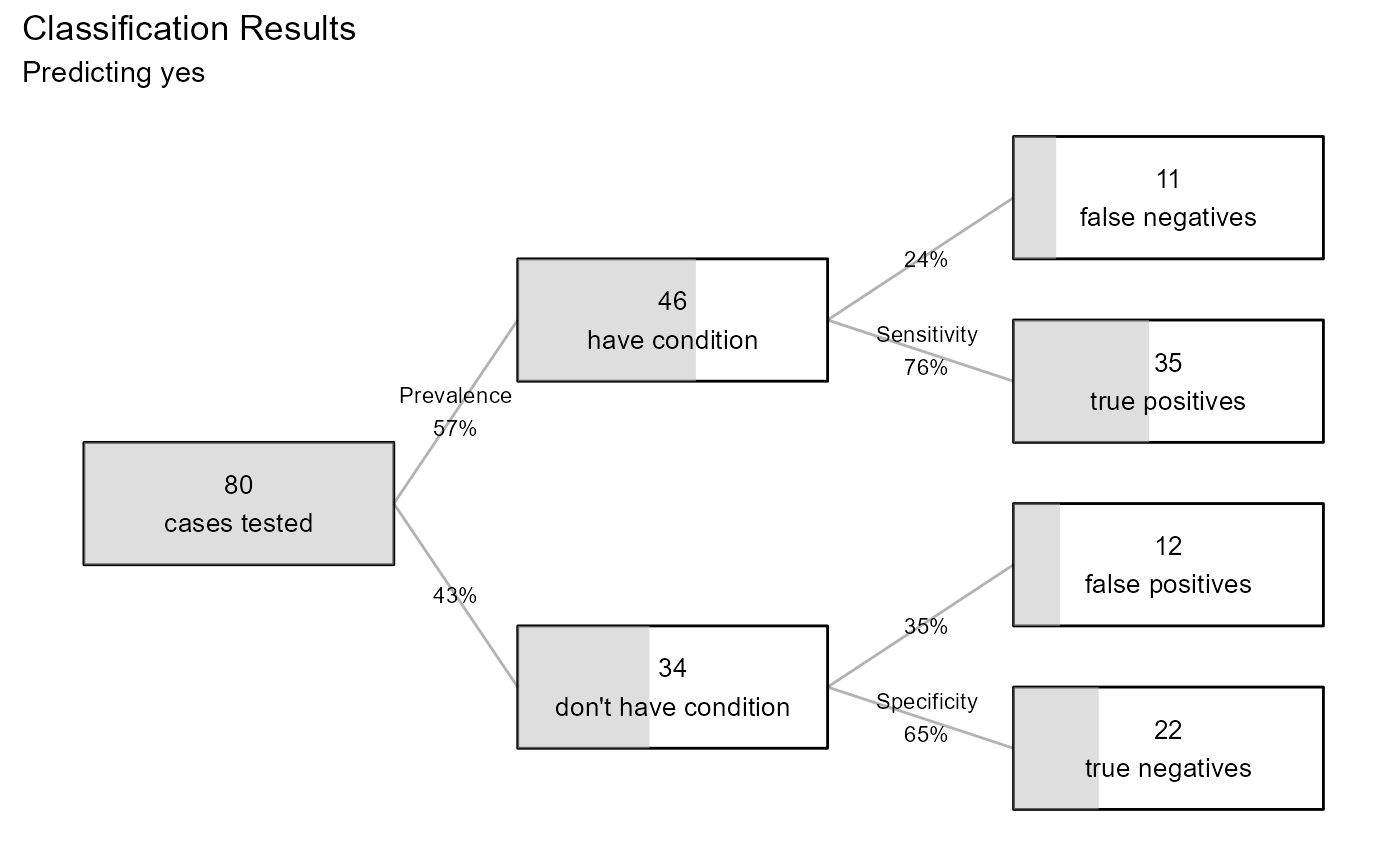
Additional output
ROC Plot
pred <- predict(fit, caesarian, type="response")
roc_plot(caesarian$caesarian, pred, positive="yes")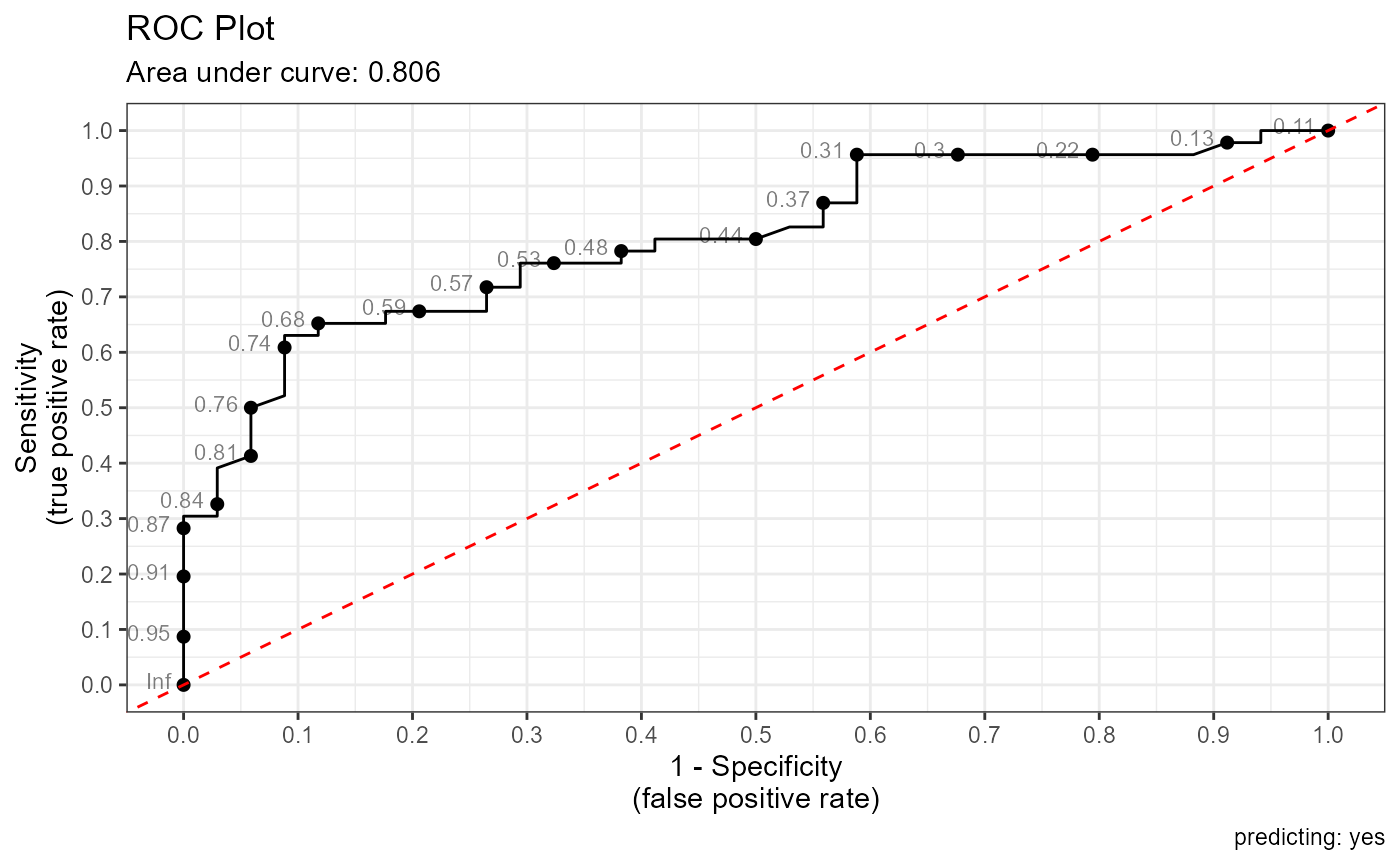
Lift and Gain Charts
lift_plot(caesarian$caesarian, pred, positive="yes")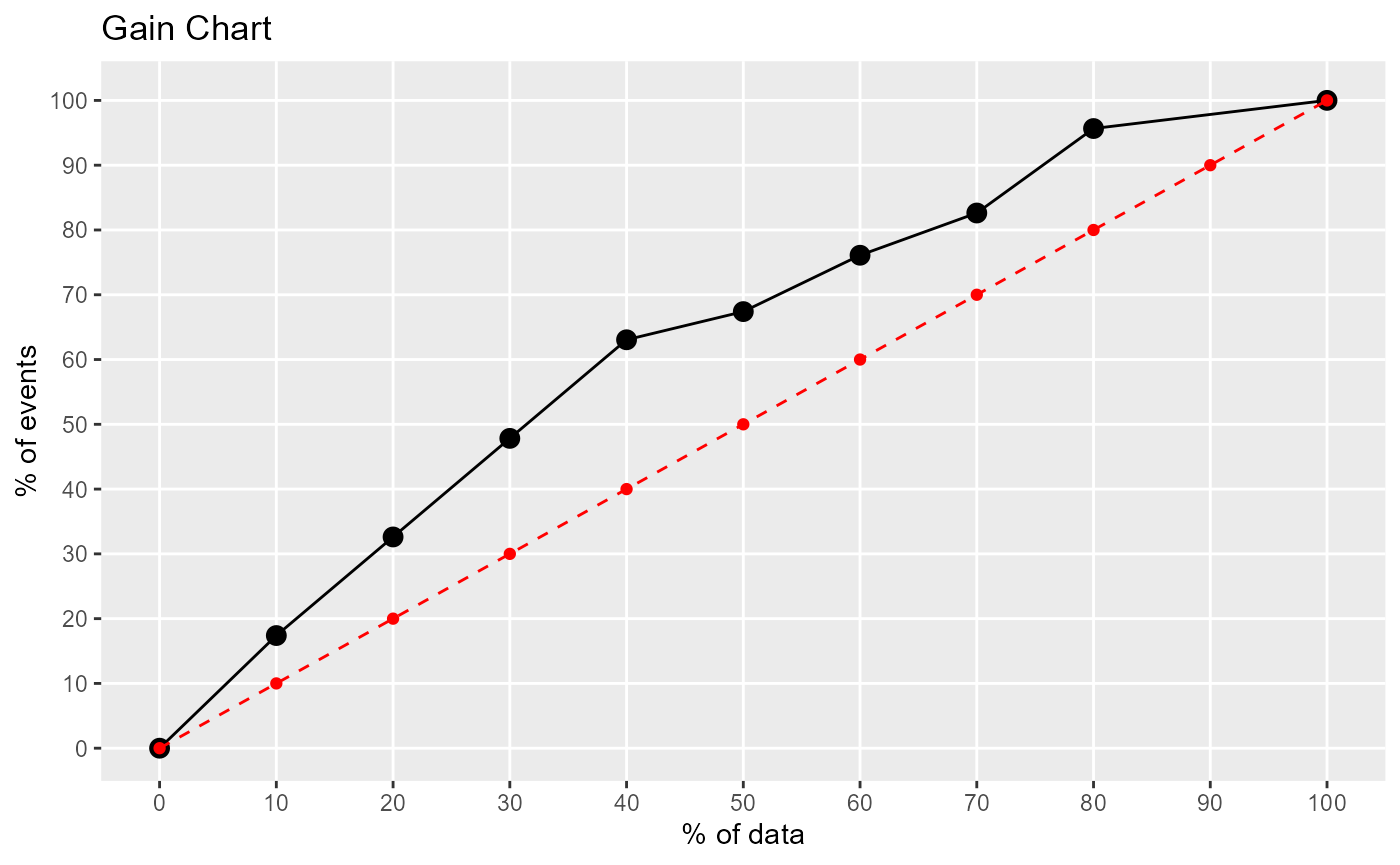
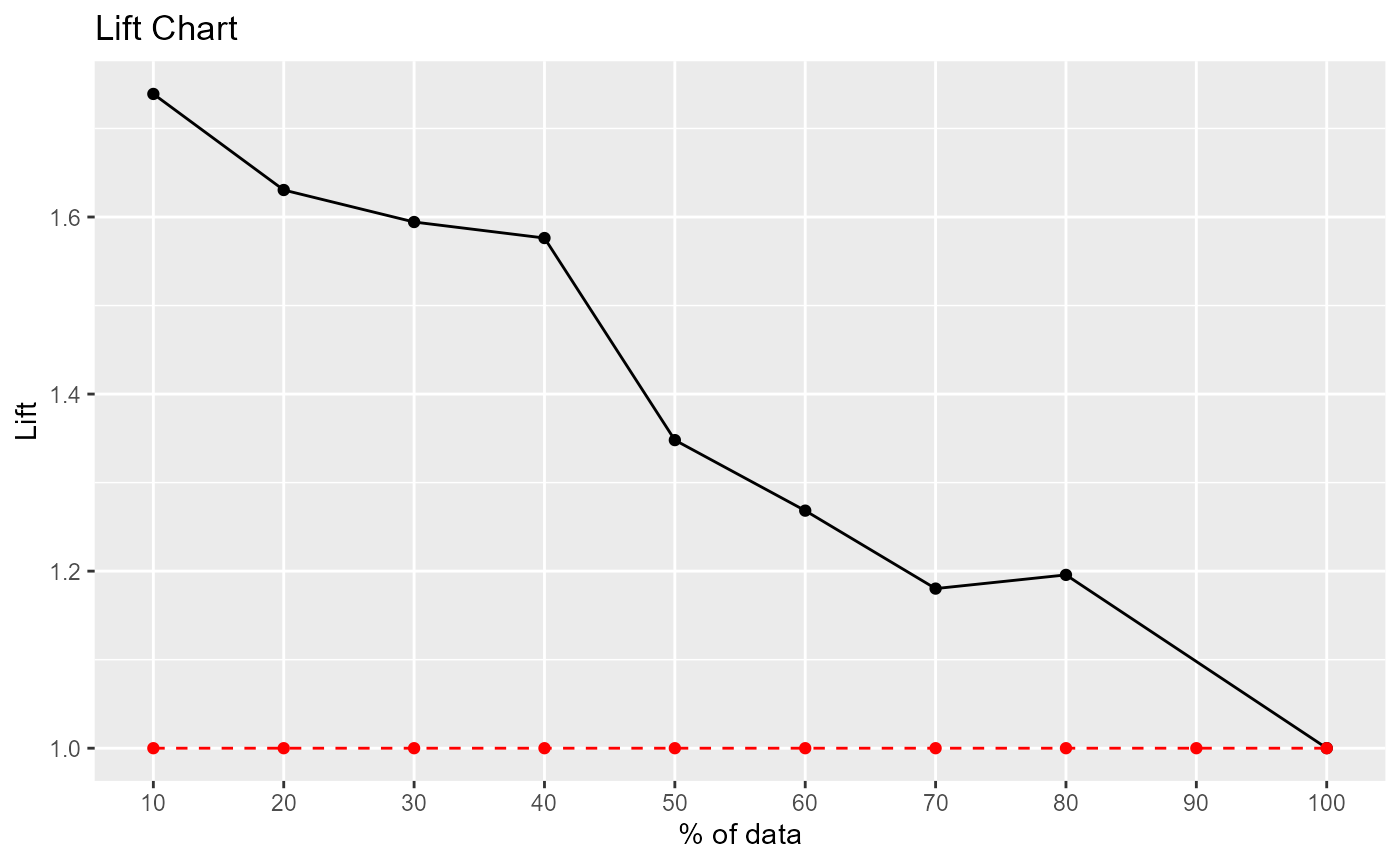
#> decile ncases nresp cumresp pctevents gain cumlift
#> 1 10 8 8 8 17.39 17.39 1.739000
#> 3 20 8 7 15 15.22 32.61 1.630500
#> 4 30 8 7 22 15.22 47.83 1.594333
#> 5 40 8 7 29 15.22 63.05 1.576250
#> 6 50 8 2 31 4.35 67.40 1.348000
#> 7 60 8 4 35 8.70 76.10 1.268333
#> 8 70 8 3 38 6.52 82.62 1.180286
#> 9 80 8 6 44 13.04 95.66 1.195750
#> 2 100 8 2 46 4.35 100.01 1.000100